Heartworm Disease
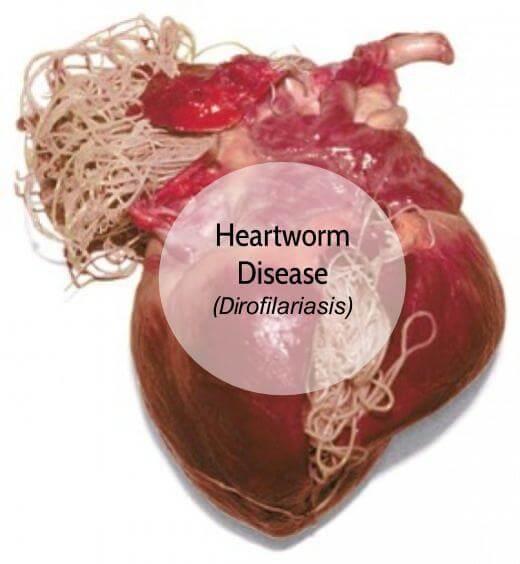
What is Heartworm Disease?
Heartworm disease is serious and potentially fatal. It is caused by a blood-borne parasite known as Dirofilaria immitis. Adult worms are found in the heart and in adjacent large blood vessels of infected dogs. .
How is heartworm disease transmitted?
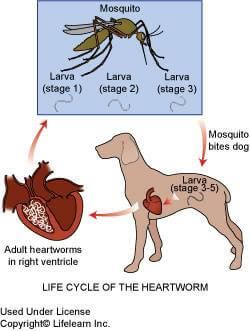
When a dog is bitten by an infected mosquito, the immature larvae (microfilaria) are injected into him. Over the course of 2-3 months, these larvae (microfilaria) mature into adult worms and eventually migrate to the heart and adjacent vessels. They start reproducing, thereby completing a full life cycle.
Mosquitos are required for transmission of the disease between dogs. The disease cannot be spread from direct dog to dog contact.
What are the clinical signs of heartworm disease?
In the initial stages of the disease there are no symptoms. As the adult worms develop and reproduce, they cause crowding of the heart and major blood vessels. This crowding reduces the blood supply to other organs of the body, particularly the lungs, liver and kidneys.
Clinical signs are dependent on the number of adult worms, the location of these worms and the length of time they have been present.
The most obvious signs are
- soft, dry chronic cough
- shortness of breath
- weakness
- lethargy
- loss of stamina
- sudden collapse during exercise and excitement (in severe cases)
How is the disease diagnosed?
There are several ways to diagnose heartworm disease
- Blood test for Heartworm Antigens
A simple in house blood test is available to test for the presence of adult heartworms. However as the antigen is only produced by mature female worms, a pure population of male or immature worms will give a false positive. - Blood test for microfilaria visualisation
A blood sample is examined under the microscope for the presence of immature larvae (microfilaria). The number of microfilaria can give us an indication on the severity of the infection. - Radiographs
Radiographs can provide some information such as enlargement of the heart and swelling of the pulmonary artery. Mature worms cannot be directly visualised on an radiograph, however this information allows us to predict the risks of complications related to treatment. - Ultrasound
An echo-cardiogram allows visualisation of the heart chambers and heartworm themselves.
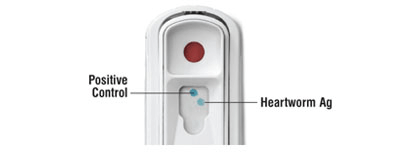 In House Heartworm Antigen Test
In House Heartworm Antigen Test
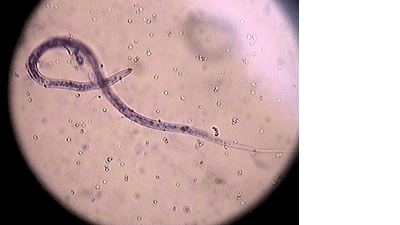 Microfilaria visualised on microscope
Microfilaria visualised on microscope
How is heartworm disease treated?
Depending on the severity of disease, treatment can take an extended period of time, ie. 6-8 months. In severe cases, the complication risk is higher and death may occur.
Treatment protocol has several steps to target the different stages of heartworm.
- Killing of immature larvae (microfilaria)
- Killing of adult worms
Complete rest is essential after each step of treatment. This is because the adult worms die and start to decompose. As they break up, they are carried in the lungs where they can potentially cause a blockage of the pulmonary vessels and cause death.
It has been attributed that death as a complication of treatment is highly related more to exercise during treatment than the treatment drug itself.
How to prevent heartworm disease?
Heartworm in dogs are easy to prevent but difficult and costly to cure. Most prevention products are designed to kill immature larvae (microfilaria) so as to inhibit maturation into adult worms.
Heartworm prevention comes in different forms and frequencies. It can be given as a monthly topical or oral medication or as a yearly injection.
Please do not hesitate to contact us at 6455 6880 if you have any queries.



